Method to track work and cost against planned performance
Earned Value method is a concise way to report the status of a project. The observed KPIs (key performance indicators) are EV, PV and AC. The calculated KPIs are SPI and CPI.
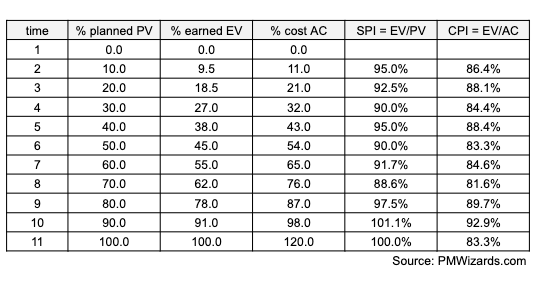
Planned Value (PV) or Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS) is the planned effort that can be converted from any units (eg.lines of code, kilometers of the road under construction) but should be treated as a percentage of the total
Earned Value (EV) or Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP) is the value earned so far. It should also be expressed in percentage.
Actual Value (AV) or Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP) is the actual cost incurred so far.
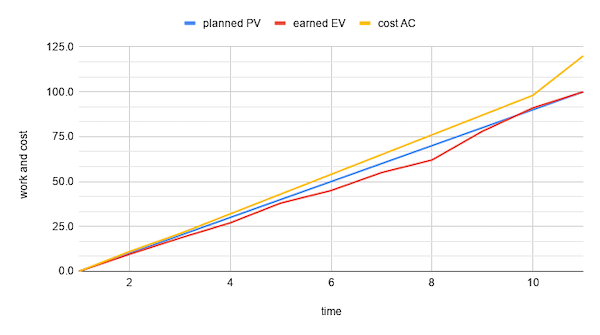
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = EV/PV is the percentage of the planned value that was earned
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = EV/AC is the percentage of the actual cost that was earned
A Schedule Performance Index above 1.0 indicates that EV > PV. This may indicate some sort of mismanagement in terms of planning or control. It can be rooted by an outdated baseline, Scope Creep or Gold Plating, since the earned value is above what was planned.
A Cost Performance Index relates the earned value with the actual expenditures. Above 1.0 indicates overcost but it should not be interpreted as a lack of control over cost. Ask yourself for the origin of the estimate: an underestimation may lead to CPI above 1.0.
Both SPI and CPI have no units (both obtained from a ratio of percentages). The target is 1.0 with a small range of flexibility according to project context, for a 5% range, KPI should be kept within the (0.95,1.05) range.
TIP:It is not possible to judge the project is a success or a failure simply by looking at these KPIS. You need to understand the success criteria before taking any decision. As a rule-of-thumb deviations from 1.0 should be well analysed and understood, regardless they are above or below 1.0.