A device to support decision under uncertainty
A decision tree is a visual device to support decision under uncertainty. The tree opens according to the available options: each branch is weighted by a probability of occurence while the leafs are possible outcomes. The decision is taken considering the Expected Value that combines the probability with the financial exposure to reach a single figure, the impact, for each branch in the tree.
For example, in the diagram below the project manager has to decide into hiring a consultant for U$ 30K to reduce the probability of a heavy expense of U$ 100,000 from 50% to just 10%. The north branch represents the decision to hire the consultant while the south branch represents the decision not to hire the consultant.
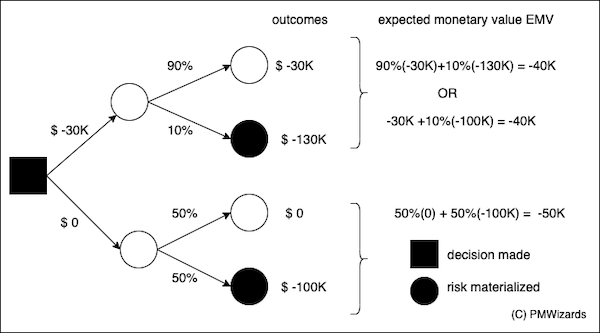
In the second step, there is the possibility of not getting the expense at 90% while the remaining 100-90=10% is that the expense still takes place. If we consider the impact of each leaf we have two costs that add together to get the outcome for the north branch: 90% x 30,000 + 10% x 130,000 = 27,000 + 13,000 = 40,000. The south branch outcome is simply 50% of U$ 100,000 that is U$ 50,000.
If the decision criteria is the lowest expected cost, the decision should be to hire the consultant since U$ 40,000 < U$ 50,000.
Back to Time Management.